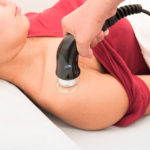
 Therapeutic ultrasound as a treatment modality that has been used by therapists over the last 70 years to treat soft tissue injuries. Ultrasonic waves (sound waves of a high frequency) are produced by means of mechanical vibration of the metal treatment head of the ultrasound machine. This treatment head is then moved over the surface of the skin in the region of the injury. When sound waves come into contact with air it causes a dissipation of the waves, between the treatment head and the surface of the skin.
As the ultrasound waves pass from the treatment head into the skin they cause the vibration of the surrounding tissues, particularly those that contain collagen. This increased vibration leads to the production of heat within the tissue. In most cases, this cannot be felt by the patient themselves. This increase in temperature may cause an increase in the extensibility of structures such as ligaments, tendons, scar tissue, and fibrous joint capsules. In addition, heating may also help to reduce pain and muscle spasm and promote the healing process.
Therapeutic ultrasound as a treatment modality that has been used by therapists over the last 70 years to treat soft tissue injuries. Ultrasonic waves (sound waves of a high frequency) are produced by means of mechanical vibration of the metal treatment head of the ultrasound machine. This treatment head is then moved over the surface of the skin in the region of the injury. When sound waves come into contact with air it causes a dissipation of the waves, between the treatment head and the surface of the skin.
As the ultrasound waves pass from the treatment head into the skin they cause the vibration of the surrounding tissues, particularly those that contain collagen. This increased vibration leads to the production of heat within the tissue. In most cases, this cannot be felt by the patient themselves. This increase in temperature may cause an increase in the extensibility of structures such as ligaments, tendons, scar tissue, and fibrous joint capsules. In addition, heating may also help to reduce pain and muscle spasm and promote the healing process.
Ultrasound is thought to accelerate the normal resolution time of the inflammatory process by attracting more mast cells to the site of injury. This may cause an increase in blood flow which can be beneficial in the sub-acute phase of tissue injury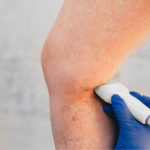 . As blood flow may be increased it is not advised to use ultrasound immediately after an injury.
Ultrasound may also stimulate the production of more collagen- the main protein component in soft tissue such as tendons and ligaments. Hence ultrasound may accelerate the proliferative phase of tissue healing.
Ultrasound is thought to improve the extensibility of mature collagen and so can have a positive effect on fibrous scar tissue which may form after an injury.
. As blood flow may be increased it is not advised to use ultrasound immediately after an injury.
Ultrasound may also stimulate the production of more collagen- the main protein component in soft tissue such as tendons and ligaments. Hence ultrasound may accelerate the proliferative phase of tissue healing.
Ultrasound is thought to improve the extensibility of mature collagen and so can have a positive effect on fibrous scar tissue which may form after an injury.
Human tissue has a relatively large absorption power for ultrasonic energy. Therefore, when ultrasonic waves are propagated in human tissues, their energy is continuously absorbed by tissues to become heat, and as a result, the temperature of the tissues themselves is increased. The heat production process is an energy conversion process in which mechanical energy is converted into heat energy in a medium, which is called endogenous heat. Ultrasound warming can increase blood circulation, accelerate metabolism, improve local tissue nutrition, and enhance enzyme activity.
Physical and chemical effects – cavitation
Both the mechanical and thermodynamic effects of ultrasound can trigger several physical and chemical changes. Cavitation forms, or maintains a stable one-way vibration, or secondary expansion to collapse, cell function changes, and intracellular calcium levels increase. Fibroblasts are activated, protein synthesis is increased, vascular permeability is increased, angiogenesis is accelerated, and collagen tension is increased. Under ultrasound, the gel can be transformed into a sol state, a softening effect on muscles, tendons, and some pathological changes associated with tissue water deficit. Such as rheumatoid arthritis and treatment of degenerative lesions of joints, tendons, and ligaments. Ultrasound can affect blood flow, inhibit, and play an anti-inflammatory effect.
 While growing up Betse worked in her dad’s Medical Office using UltraSound on the athletes. Both the athletes and Betse were amazed at the results. The contusions and painful areas on their body benefited from the treatment.
While growing up Betse worked in her dad’s Medical Office using UltraSound on the athletes. Both the athletes and Betse were amazed at the results. The contusions and painful areas on their body benefited from the treatment.
If you would like to experience the UltraSound for yourself and live near Oceanside, California contact Betse. During COVID 19 this will be done outside with masks on and 6 feet apart.
